Classification
HOW DO YOU CLASSIFY A VELVET BEAN?
DOMAIN: Eukarya
The domain Eukarya is classified by cells that have a true nucleus surrounded by its nuclear membrane. Eukaryotes also contain membrane bound organelles.
KINGDOM: Plantae
The distinguishing characteristic of the kingdom Plantae is that the cells have a cell wall made of cellulose used for supporting the plant. Most members of this kingdom are autotrophic and use photosynthesis to obtain its nutrients. Members of this kingdom also demonstrate a unique life cycle called alternation of generations, which means they have both a multicellular haploid and multicellular diploid stage.
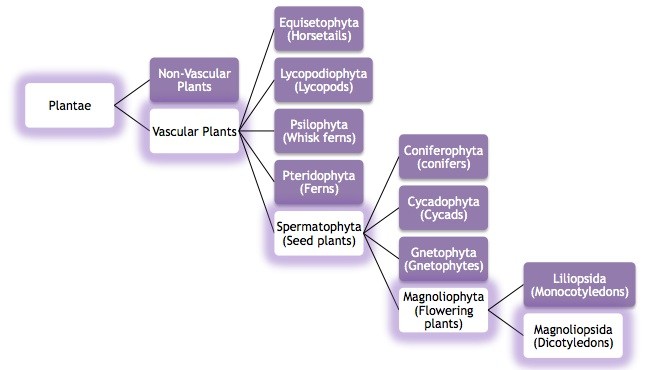
This image above diagram (computer generated by Emily Probst) shows the classification of the velvet bean through the different types
of plant groups. This classification was based solely on morphological characteristics, or the appearance of the velvet bean.
PHYLUM: Magnoliophyta
These plants consist of flowering plants called angiosperms. The seeds of angiosperms are contained in the fruit, while pollination occurs with the help of wind, water, or other organisms.
CLASS: Magnoliopsida
Plants of this class are referred to Dicotyledons. Below is a table I created to allow you to get a better understanding of the differences between monocotyledons and dicotyledons.Some examples of other dicots are the opium poppy and the purple passion flower, and some examples of monocots are orchids, jack-in-the-pulpit, and sweet corn.
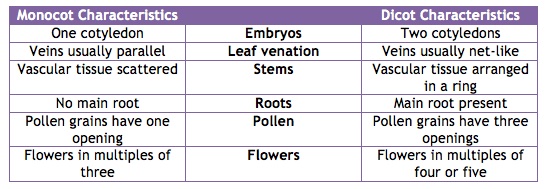
Chart computer generated by Emily Probst.
ORDER: Fabales
Members of the order Fabales are known as legumes, or bean plants. A common feature of most legumes is there ability to live in poor soil conditions because of their symbiotic relationship with bacteria. You will learn more about this symbiosis later in the Interactions page.
FAMILY: Fabaceae
Fabaceae is the most important plant family for producing food for humans and livestock. The fruit of these plants is typically called pods, which is a single seed bearing carpel (the female reproductive organ) that splits open along two seems. The flower is usually butterfly-like, with unequal petals, situated in an upright position.
GENUS: Mucuna
The genus Mucuna is made up of around 100 species of tropical vines. The premature seedpods are covered in fuzzy, microscopic hairs that help protect the plant from seed predators. The seeds are also full of toxic levels of amino acid L-dopa, which can be harmful to animals and even humans. Most species of Mucuna are pollinated by night-flying bats.
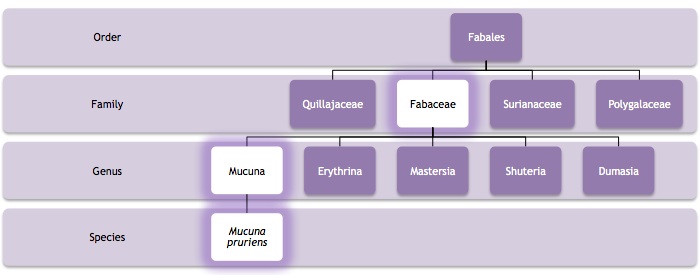
This diagram (computer generated by Emily Probst) shows the phylogeny of the Mucuna genus based on molecular data. The gene that was sequenced is
called the rbcL gene, and it plays an important role in understanding the phylogeny, or genetic make-up of other legumes similar to Mucuna pruriens.
SPECIES: Mucuna pruriens
This tropical legume is known for its extreme itchiness when coming in contact with the plant. Mucuna pruriens bears white, lavender, or purple flowers. The most important use of the Mucuna pruriens is its use in growing crops, but it is also known for its variety of medicinal uses.
To find out if the velvet bean is found near you, click on Habitat.