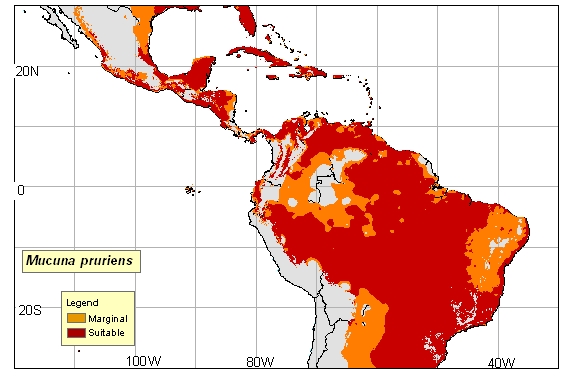
Habitat
WHERE DO VELVET BEANS LIVE?
The velvet bean is India’s most popular drug, and it is used in over 200 types of drugs. It is native to areas in southern China and Central and South America, as seen in the picture below. Now, it is also widely distributed to other areas of the world such as the West Indies, tropical American, the Pacific Islands, and the United States. Another example of a plant that lives in tropical areas, such as India, is the black pepper.
Mucuna pruriens can grow in very diverse environments. It prefers well-drained soil, but can also grow in sandy soils and soils with great acidity range. Mucuna prefers hot, climates with rainfall ranging between 1,000-2,500 mm, but also can grow in as little as 400 mm of annual rainfall. It does have some tolerance to drought, but Mucuna will not survive in very saturated soils. The best temperature range to grow Mucuna pruriens is between 19-27°C and requires high light intensity to grow.
photo provided by Michael Peters
The velvet beans are climbing vines called lianas that intertwine through the rain forest trees. Their flowers and pods are formed on long, rope like stems that hang from the forest canopy. In less tropical environments, such as the United States, the velvet bean grows alongside other farming crops in fields. It also has the ability to grow on hedges and bushes, as seen in the picture in the bottom right.
The velvet bean growing on vines in Brazil The velvet bean growing among hedges and bushes in the tropics.
Photo provided by Dinesh Valke. Photo provided by Lalithamba.
To find out how the velvet bean can adapt to the environment it lives in, click Adaptation.