
Reproduction
![]()
![]()
![]()
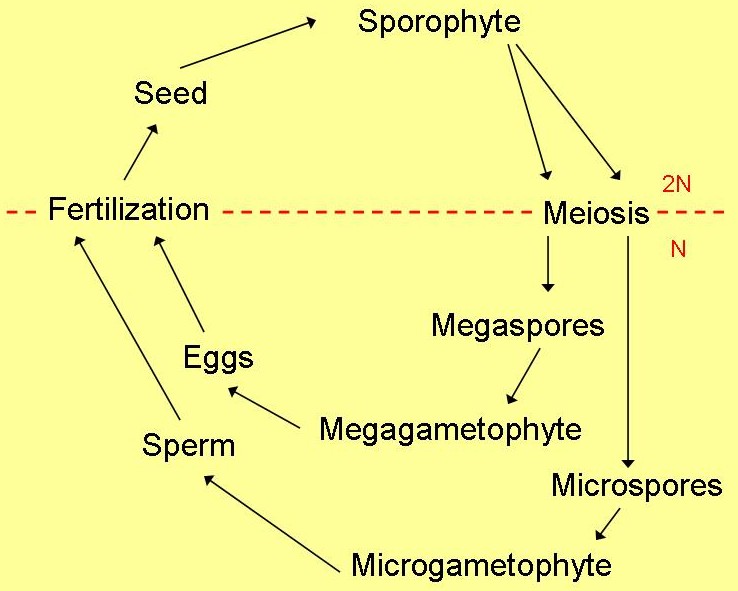
The life cycle of
Allium sativum can be defined by the different stages
shown to the left. Above the dashed red line shows the diploid stages and
below the line shows the haploid stages. During the diploid stages is when
all
the actually growing of the plant takes place. The haploid stages are that
of
the separation of the two different sex orientations. The majority of the
time
is spent in the diploid stage of its life cycle.
The only thing with Allium sativum is that it
has become infertile over the
many years of cultivation. Wild versions are still fertile in most cases,
but
there is not very much wild Allium sativum, just like there is not
very much
wild
Zea mays.
Both are monocots and go through basically the same life
cycle, however have very different ways of going about their life style.
See
the link on Zea mays for its information.
 The image to the left shows the flower of Allium sativum just before it
is about to blossom and the image to the right shows Allium sativum
blossoming. It makes a beautiful small white flower that would be perfect for
any bouquet.
The image to the left shows the flower of Allium sativum just before it
is about to blossom and the image to the right shows Allium sativum
blossoming. It makes a beautiful small white flower that would be perfect for
any bouquet.
![]()


If you have any questions, comments, or found any errors, please email me at gallant.kirk@students.uwlax.edu.