Classification

Kali Fleischauer 2013.
Domain - Eukarya
Each cell of Galerina autumnalis contains
membrane-bound organelles, DNA in chromosomes enveloped within
a nucleus, and produces cells through means of mitosis. These
characteristics are all qualities that are found in Eukarya.
Toxicodendron radicans (poison ivy), is also an example of a Eukarya.
Click
here to read about poison ivy!
Kingdom -Fungi
Fungi are a kingdom within the Eukarya which possess cell
walls constructed from chitin, unlike plant cell walls composed of
cellulose. Spores are produced commonly in methods of reproduction
for fungi. Rhizopus stolonifer (Black
bread mold) is also a member of
the fungi kingdom.
Phylum - Basidiomycota
This phylum contains mushrooms, puffballs, bracket fungi,
stinkhorns, and more.
This phylum contains organisms with the general structures
of a mushroom such as the cap, gills, and stipe. In means of sexual reproduction, basidiomycota have basidia
found
on the outermost layer of cells that make up the gills. These basidia produce haploid basidiospores. This method of reproduction
is specific to this phylum and contributes to the
phylum's name. To learn more about the reproductive life cycle of
Galerina autumnalis check out the
reproduction page. Lepiota
josserandii (The Deadly Parasol) also belongs to this phylum.
Click
here to learn more about the Deadly Parasol.
Class - Agaricomycetes
This class is known to contain one of the oldest and
largest basidiomycota. This mushroom is known as
Armillaria gallica.
Click here to learn more about
the relationship between Armillaria gallica and
Galerina autumnalis. A large portion of this class are said to
be wood-decaying or ectomycorrhizal symbionts with animals or
plants. Examples of agaricomycetes can be found throughout
terrestrial environments. Agaricus bisporus (Button
Mushroom),the mushroom that is commonly found on pizza, is in this
class as well.
Order - Agaricales
A main characteristic of agaricales is a fleshy-like
exterior along with the structures such as the stalk, cap, and
gills. The basidiospores in this order are typically dispersed by
wind once they fall from between the gills. Cantharellus cibarius (Chanterelle
mushroom) is also a member of this order.
Family - Strophariaceae
These gilled mushrooms have spores which are generally brown
in color. Most members have mycorrhizal mutualism with plant roots. Most of this family contains a toxin of some
sort and as a result people are advised to not consume this family
of fungi.
Gymnopilus spectabilis is a member of this family who
shares a similar cap color with Galerina autumnalis.
Genus - Galerina
Most of this genus are found in temperate regions. Go
to the habitat page to further read about
the Galerina autumnalis habitat. Generally,
Galerina is found in association with moss along with being a
decomposer of wood. This genus is polyphyletic meaning it descends
from more than one recent ancestor. A greater sense of diversity is
found within this genus as a result. Click here
to further investigate some facts about Galerina autumnalis
and other members of the genus.
Species - Galerina autumnalis*
This species is significant because it is commonly
found on the ground growing over buried, decaying wood around early
spring and late fall. The Latin word autumnalis
refers to the mushroom blooming in the fall. It has received the
common name Deadly Galerina in result of the increasing
knowledge of G. autumnalis's deadly effects.
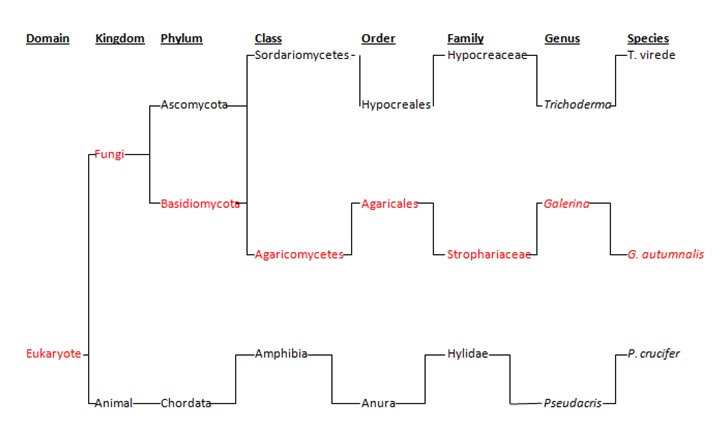
Kali Fleischauer 2013.
This phylogenetic tree is based off of genetic similarities. The
examples
are said to share at least one protein sequence in common with the
ones they are attached to. The red
names
are the route in which Galerina autumnalis classification
takes in this image of classification. The other names involved are examples of what
else are found in the classification. This is done to provide a
better understanding of other examples that can be found in the
classifications.
From left to right the tree shows the domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species of
Galerina autumnalis.
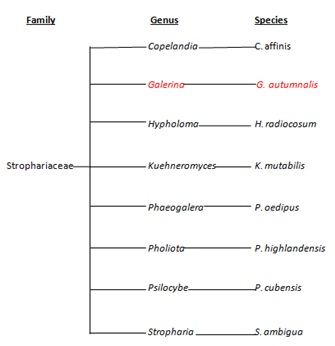
This tree to the right is an explanation of the genera and species found within the family of strophariaceae. G. autumnalis is found under the genus of Galerina along with other species under their corresponding genus.
*NOTE* After a study in 2001, it has been documented that Galerina autumnalis and Galerina marginata along with a few other members of the genus are genetically the same species (Gulden, 2001). The names of the mushroom are interchangeable.
Kali Fleischauer 2013.
