Classification
Click any one of the following to link to a specific topic.
● Taxonomy
Tree Swallows fall into these groupings:
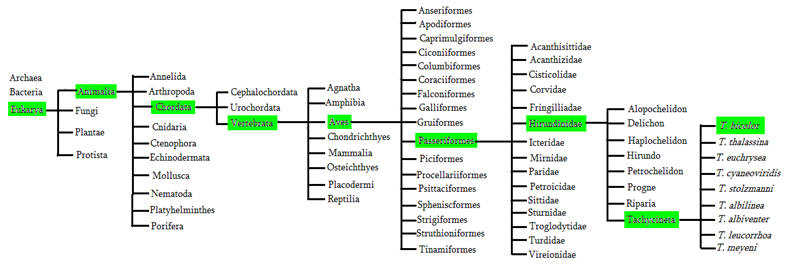
Domain -
Eukarya
Kingdom
- Animalia
Phylum -
Chordata
Class -
Aves
Order -
Passeriformes
Family -
Hirundinidae
Genus -
Tachycineta
Species
– Tachycineta bicolor
At first glance this could seem unimportant to anyone that hasn't taken an Organismal Biology course, but each of these groups have their importance to this organism and to any other organisms that also fall under it as well. The explanation for why Tree Swallows fall into each group is found below.
Domain - Eukarya
There are three domains total that we classify all organisms
of life in.2.jpg) These include Eukarya, Archaea, and Bacteria.
While Archaea and Bacteria include organisms that are prokaryotic,
Eukarya includes all organisms that are eukaryotic.
At the cellular level, eukaryotic organisms have a type of cell with a
membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles.
These are two features not found in prokaryotic organisms.
These include Eukarya, Archaea, and Bacteria.
While Archaea and Bacteria include organisms that are prokaryotic,
Eukarya includes all organisms that are eukaryotic.
At the cellular level, eukaryotic organisms have a type of cell with a
membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles.
These are two features not found in prokaryotic organisms.
Kingdom - Animalia
Just like the name implies, the Kingdom Animalia contains organisms classified as animals. But what makes an animal an animal, at least scientifically? Well, animals are organisms that are multicellular and must ingest their food. Other distinguishing characteristics of animals are that they lack the rigid cell wall found in other phyla. Also, all animals are motile at some point in their life stages, even if just for one stage.
Phylum - Chordata
Animals can then be separated further by  this phylum.
All organisms that fall under the Phylum Chordata have five defining structures during some
point in their development. These five structures include: a notochord, a
hollow dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal gill slits, an endostyle, and a
post anal tail. In humans, these structures will give rise to
intervertebral disks, brain and spinal cord, structures in ear and throat,
thyroid gland, and coccyx, respectively.
this phylum.
All organisms that fall under the Phylum Chordata have five defining structures during some
point in their development. These five structures include: a notochord, a
hollow dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal gill slits, an endostyle, and a
post anal tail. In humans, these structures will give rise to
intervertebral disks, brain and spinal cord, structures in ear and throat,
thyroid gland, and coccyx, respectively.
Class - Aves
The taxa Aves associates with the organisms that have the characteristics of modern birds. These organisms have feathered wings, two legs that are used for walking or standing, are warm-blooded, and lay eggs.
Order - Passeriformes
The Order Passeriformes is designated to all perching songbirds. These organisms have adapted claws for sitting for long periods of time and adapted voices for singing to other birds. The order consists of more than half of all species of birds which makes it the largest order of birds.
Family -
Hirundinidae
This taxa includes the swallows and martins. These birds are characterized by
their adaptation to feeding in the air.
Genus -
Tachycineta
The word Tachycineta means “swift move.”  This is a
characteristic of all swallows. The Genus Tachycineta separates birds
into just the swallow group which are characterized by their forked tails and
all white underbody. Including their body characteristics, these swallows
separated from other swallows based on their range and their nesting.
Swallows under Tachycineta are only found in North, South, and Central
America and use natural or disused cavities for nests sites.
This is a
characteristic of all swallows. The Genus Tachycineta separates birds
into just the swallow group which are characterized by their forked tails and
all white underbody. Including their body characteristics, these swallows
separated from other swallows based on their range and their nesting.
Swallows under Tachycineta are only found in North, South, and Central
America and use natural or disused cavities for nests sites.
Species – Tachycineta bicolor
Bicolor means “two colors.” Two colors could be indicative to the two different colors of the female Tree Swallow which they have a dull brown back when immature and metallic blue back as an adult. Both still have a white underbelly.
(All the names of the Order and Family of Tachycineta
bicolor are not included. Click
Order or
Family to link to a website with the entire link.)
This phylogenetic tree goes through stepwise starting with the widest grouping including all organisms to the narrowest including just the swallows. Refer to Taxonomy.
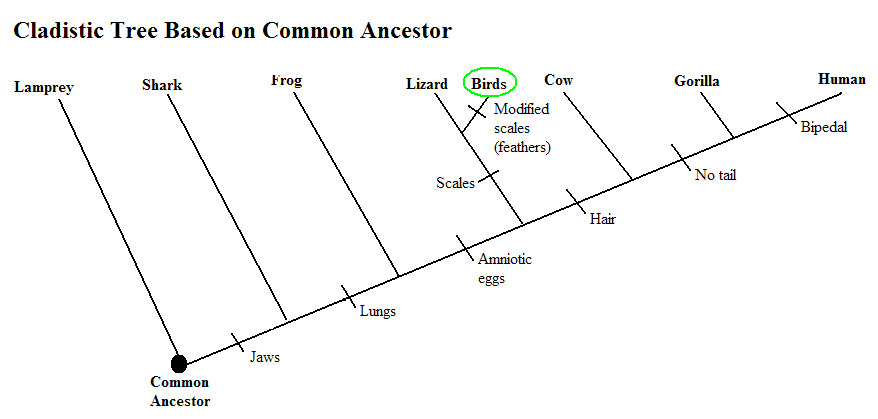
This cladistic tree relates many organisms falling into
.jpg) the
Phylum Chordata based on the traits they possess. This tree takes an
approach that separates these organisms through their evolutionary
relationships. As can be seen , each diagonal line represents an organism.
Some of these lines have traits coming off of that line. These traits
indicate a shared derived trait that all the organisms that follow that line
share. So, for example, the lines that follow the trait hair all have that
trait. These organisms include Cow, Gorilla, and Human. This also
means that the organisms behind do not possess this trait. Lamprey is the
most primitive and lacks all the traits, based on this tree. Every spot
where two lines converge indicates a common ancestor to those organisms.
the
Phylum Chordata based on the traits they possess. This tree takes an
approach that separates these organisms through their evolutionary
relationships. As can be seen , each diagonal line represents an organism.
Some of these lines have traits coming off of that line. These traits
indicate a shared derived trait that all the organisms that follow that line
share. So, for example, the lines that follow the trait hair all have that
trait. These organisms include Cow, Gorilla, and Human. This also
means that the organisms behind do not possess this trait. Lamprey is the
most primitive and lacks all the traits, based on this tree. Every spot
where two lines converge indicates a common ancestor to those organisms.
For birds, including Tree Swallows, they all possess
the traits: Jaws, Lungs, Amniotic eggs, Scales, and Modified Scales (feathers).
As can be seen through this Cladistic Tree, Birds and Reptiles evolved from a
common ancestor. Birds are separated from reptiles based on their modified
scales (feathers), along with other traits that are not indicated on this tree,
allowing them to fly.
To learn more about Tree Swallows click General Information. Click here to return return to the Tree Swallow:Tachycineta bicolor Homepage.