Taxonomy/Phylogeny:
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
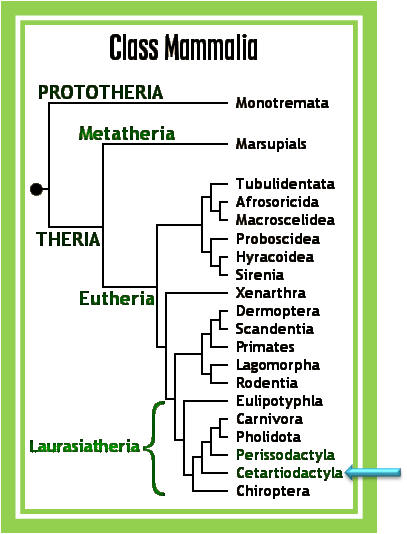
Class: Mammalia
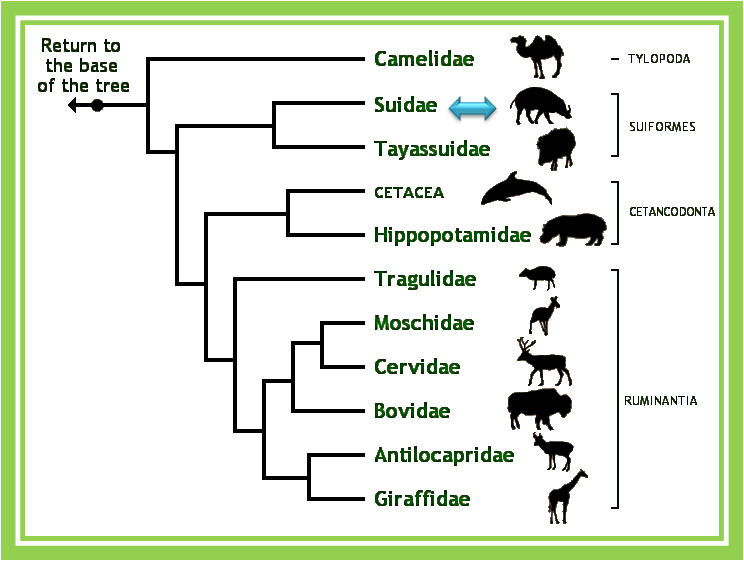
Order: Cetartiodactyla (Even-toed animals ; includes Swine,
Peccaries,
Hippopotamuses,
Camels,
Deer, Giraffes, Cattle, Goats,
and
Sheep)
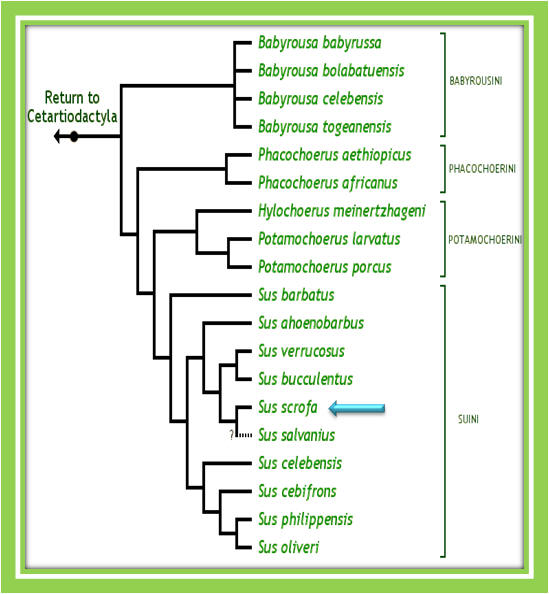
Family: Suidae
Genus: Sus
What does it all mean?
Eukarya: Includes all of the organisms with eukaryotic cells--that is, those with membranous organelles (including mitochondria and chloroplasts).
Animalia: All members of the Animalia are multicellular, and all are heterotrophs (that is, they rely directly or indirectly on other organisms for their nourishment). Most ingest food and digest it in an internal cavity.
Chordata: Chordates are defined as organisms that possess a structure called a notochord, at least during some part of their development.
Mammalia: All mammals share at least three characteristics not found in other animals: 3 middle ear bones, hair, and the production of milk by modified sweat glands called mammary glands.
Some relatives in the class Mammalia include:
Primates Marsupials Rodents Serenia
Cetartiodacyla: Cetartiodacyla are paraxonic, that is, the plane of symmetry of each foot passes between the third and fourth digits. In all species the number of digits is reduced at least by the loss of the first digit, and the second and fifth digits are small in many. The third and fourth digits, however, remain large and bear weight in all Cetartiodactyls.
Some relatives in the order Cetartiodacyla include:
Giraffidae Hippopotamidae Cetacea
Suidae: Sixteen species of pigs and hogs in eight genera make up the modern family Suidae
Some relatives in the family Suidae include:

***Note all Phylogenetic Trees featured are based from molecular data***