Plays Well With Others
Salmonella enteritidis is a parasitic organism which benefits from living inside the host, but it harms the host in the process. As mentioned on the home page, raw eggs are very common hosts to Salmonella.
There are two different ways that hen eggs become infected:
-
First, if the shell of the egg comes in contact with any feces of an infected hen, the Salmonella can penetrate the egg shell through tiny pores, or get inside via any cracks on the shell.
-
Second, Salmonella enteritidis can also enter through the cloaca and travel up to the reproductive organs of the hens.
S. enteritidis has been found in the intestins, ovaries, oviduct, and peritoneum of infected hens as well. Salmonella enteritidis has unique adaptations that allow it to survive attacks from antimicrobial factors. If it survives the attacks, S. enteritidis will then travel from the egg white to the yolk. This adaptation is thought to be a result of a unique combination of genes that improves the strength of the cell wall.

Once
Salmonella
strains enter the stomach via oral ingestion, they penetrate the
mucosal barriers of the intestines.
Salmonella
target the specialized antigen transporting membrane cells (M
cells) which are located among the mucous cells.
They then enter the host tissues, bind to the cells
lining the gut, begin to grow, and use the M cells for their
own use. They begin
to multiply while invading the intestinal tissues and produce an
enterotoxin which causes an inflammatory reaction, leading to
diarrhea.
S. enteritidis
is a heterotrophic organism which means that it does not
produce its own food.
It gains nutrients by feeding inside of the host.
Effects on humans
Infants and elderly are at the highest risk for being affected
by Salmonella as
their immune systems are generally the weakest.
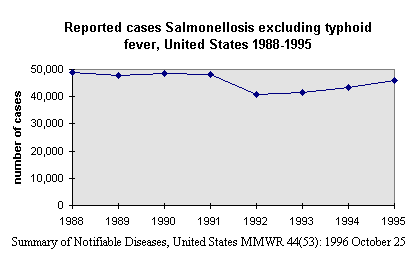
It is estimated that 2 to 4 million cases of salmonellosis occur
in the
 Initial symptoms may persist 3-7 days and include:
Initial symptoms may persist 3-7 days and include:
Nausea
Vomiting
Abdominal cramps
Diarrhea
Fever
Headache
Chronic problems may usually occur 3-4 weeks after initial symptoms and may include:
Arthritis
Joint swelling
Reducing Pit Stops
Antibiotics are used to rid the infected human or animal of the bacteria. In the past, our nation overused antibiotics. Natural selection acts on the bacteria and kills off the majority of them when they are exposed to the antibiotic. However, some of the bacteria are better-suited to survive. They then reproduce, which is done very fast, especially for these prokaryotic bacteria. As generations elapse, the population will eventually develop immunity to these drugs that were first introduced to kill the bacteria. It is through these adaptations that these bacteria are such a growing problem to the human population.
Copyright Dennis Kunkel Microscopy, Inc.
For example, in many large scale farming operations, cows and
pigs are fed antibiotics from a very young age.
This is cheaper for the farmer in the short term as these
animals appear healthier and can grow faster.
However, these bacteria develop resistance fairly quick.
page by clicking on the link below:
Domestic cow