Classification

Domain:
Eukarya
Kingdom:
Animalia
Phylum:
Arthropoda
Class:
Insecta/Hexapoda
Order:
Hymenoptera
Family:
Formicidae
Genus:
Eciton
Species:
Eciton hamatum
Phylogenetic tree of similar organisms.
Why is it classified as such?
Eukarya?
This species belongs to this domain because it is a multi-cellular
organism and its cells contain a true nucleus and membrane bound
organelles. Another fascinating organism you should check out in the
domain eukarya is
Chironex fleckeri (Australian box jellyfish).

Kingdom?
Animals that are classified in animilia, such as
Eciton hamatum,
lack rigid cell walls and most have specialized tissues (except for
sponges, they are totapotent). They are all multicellular and are
nearly all organisms in the kingdom are heterotrophic. Look at
another neat organism within the animilia the
Hispaniolan solenodon.

Phylum?
Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical protostomes and have a
segmented body. The body is split into three different parts
consisting of the head, thorax, and abdomen. The body of arthropods
are supported by an exoskeleton covering made of chitin. Check
another cool member of the arthropods
Sicarius hahni
(The Six-Eyed Sand Spider).
Class?
The hexapods are the most vast group of any class with approximately
1 million species named and an estimated several times that number
unnamed or found the class varies greatly. Insects are composed of a
head, thorax, abdomen, compound eyes, antennae, and three pairs of
walking legs. Hexapods lack musculature beyond the first segment of
antenna, have a complete complete digestive tract, breathe with a
tracheal tube system, have spiracles, and must molt. This molting is
the shedding of the exoskeleton to grow or to undergo a
metamorphosis. Check out another member of hexapods that is
poisonous, the
Battus philenor
(Pipevine Swallowtail).

Order?
Hymenoptera are defined by two pairs of wings that have fewer veins
than other insect groups and the abdominal tergum is connected to
the metanotum. This grouping classification consists of mostly bees,
wasps, and ants.
Family?
The common characteristic of the formicidae is the evolution of a
metapleural gland. This gland helps to defend the ant against
bacteria and fungus. Some members of the formicids, which are ants,
have lost this gland so their are some exceptions, typically these
exceptions are found in very dry and arid environments. Another
important feature of the formicids is their body structure,
formicids are distinguished by the waist, which is "pinched down"
posteriorly where it connects to the abdomen. In addition they have
a very developed social system which very few other insects have
developed.
Genus?
Eciton are highly polymorphic, have single facet
eyes, a strongly developed sting and falcate mandibles which define
the genus.

Species?
The specie E. hamatum can be distinguished by its
large horns on the rear of the head that protect the neck from other
ants with which it may fight. Its coloring is also much different
from other Eciton species E. hamatum displays
colors of burnt sienna and orange.
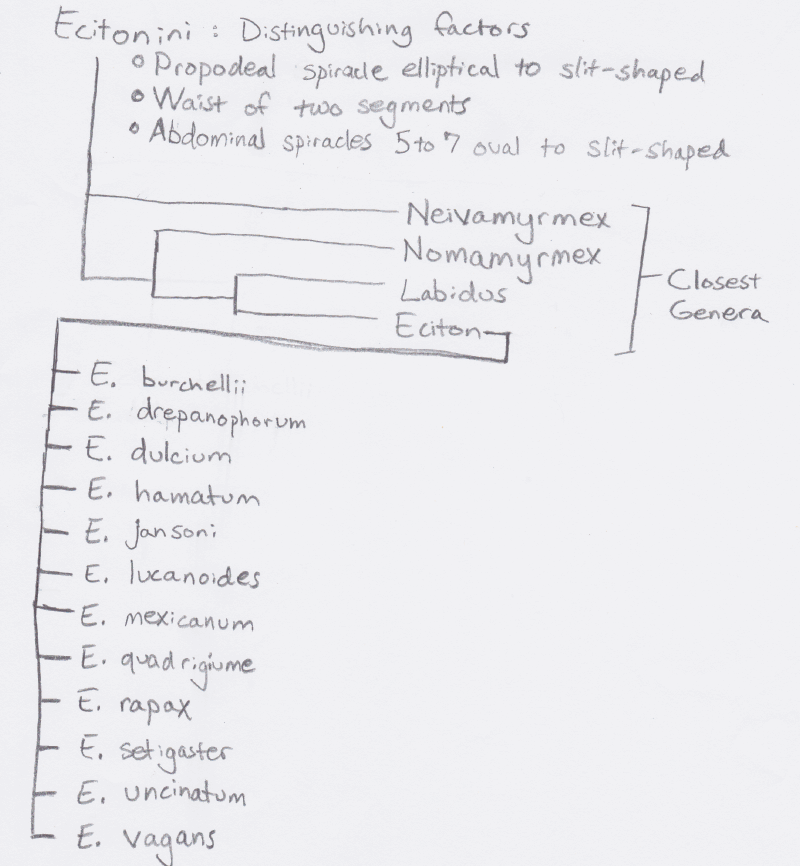
Closest genera under the
subfamily Ecitoninae, these genera are all members of the tribe
Ecitonini. The tree also contains all of the species in the genus
Eciton.
Learn more about the classifications of animals check out this cool
site the
Animal Diversity Web!
Here is an poisonous intriguing organism that is not in the eukarya
the
Plesiomonas shigelloides.