|
Molecules involved in translation
Translation is a process where genetic information is translated from a ``nucleic acid language" to an
"amino acid language". Translation is catalyzed by a large enzyme
called a ribosome,
which contains proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Translation also involves specific RNA molecules called transfer RNA (t-RNA) which can bind to
three basepair codons on a messenger RNA (mRNA) and also carry the appropriate amino acid encoded by the codon.
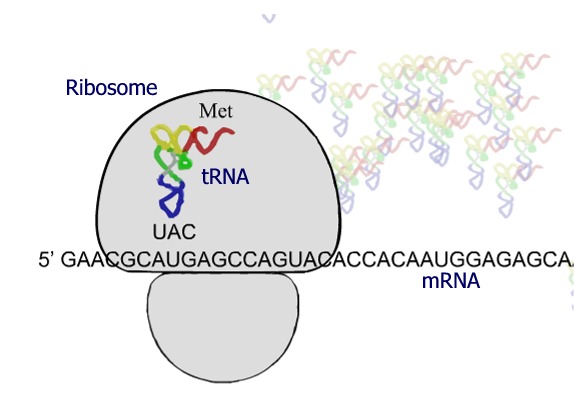
The ribosome assembles on the first AUG (start codon) in the mRNA. This
codon encodes the amino acid methionine (Met).
Open Reading Frame
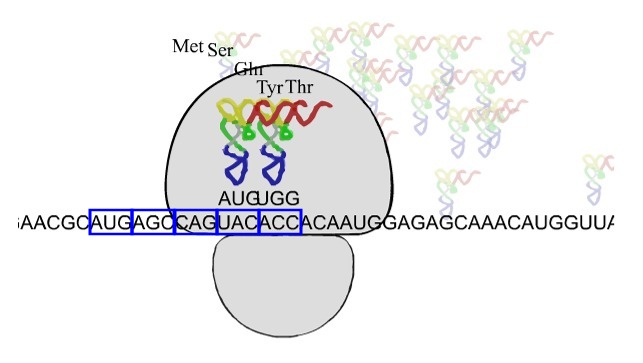
Once the start codon is identified, each sequential group of three base
pairs form the next codon. In this way the position of the start
codon determines the open
reading frame, or order of codons that will be read to form the
protein. In the example below, once the ribosome assembles on the
first AUG, the order of the rest of the codons is set for the rest of the
translation of the mRNA.
The Genetic Code
The 1968 Nobel
Prize in Medicine was awarded for deciphering the Genetic Code. The
genetic code is used to translate three base codons in RNA or DNA (recall that
U=T in RNA and DNA respectively) into amino acids (given in their three letter
and one letter codes). Scientists now use computer programs to translate DNA sequences into predicted amino acid sequences.
Translation stops when a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) is reached, and a
termination factor causes the ribosome to dissociate from the mRNA.
|
First
Position
|
|
Second
|
Position
|
|
Third
Position
|
|
|
U
|
C
|
A
|
G
|
|
|
|
Phe
(F)
|
Ser
(S)
|
Tyr
(Y)
|
Cys
(C)
|
U
|
|
U
|
Phe
(F)
|
Ser
(S)
|
Tyr
(Y)
|
Cys
(C)
|
C
|
|
|
Leu
(L)
|
Ser
(S)
|
Stop
|
Stop
|
A
|
|
|
Leu
(L)
|
Ser
(S)
|
Stop
|
Trp
(W)
|
G
|
|
|
Leu
(L)
|
Pro
(P)
|
His
(H)
|
Arg
(R)
|
U
|
|
|
Leu
(L)
|
Pro
(P)
|
His
(H)
|
Arg
(R)
|
C
|
|
C
|
Leu
(L)
|
Pro
(P)
|
Gln
(Q)
|
Arg
(R)
|
A
|
|
|
Leu
(L)
|
Pro
(P)
|
Gln
(Q)
|
Arg
(R)
|
G
|
|
|
Ile
(I)
|
Thr
(T)
|
Asn
(N)
|
Ser
(S)
|
U
|
|
|
Ile
(I)
|
Thr
(T)
|
Asn
(N)
|
Ser
(S)
|
C
|
|
A
|
Ile
(I)
|
Thr
(T)
|
Lys
(K)
|
Arg
(R)
|
A
|
|
|
Met
(M)
|
Thr
(T)
|
Lys
(K)
|
Arg
(R)
|
G
|
|
|
Val
(V)
|
Ala
(A)
|
Asp
(D)
|
Gly
(G)
|
U
|
|
|
Val
(V)
|
Ala
(A)
|
Asp
(D)
|
Gly
(G)
|
C
|
|
G
|
Val
(V)
|
Ala
(A)
|
Glu
(E)
|
Gly
(G)
|
A
|
|
|
Val
(V)
|
Ala
(A)
|
Glu
(E)
|
Gly
(G)
|
G
|
Try matching the following codons
to their respecitve amino acids.
Steps in Translation
- The following movie illustrates the translation of a mRNA by a ribosome
and tRNAs. Note that the ribosome assembles on the first AUG (start codon)
in the mRNA. Once the start codon has been identified, the rest of the
codons in the mRNA are read sequentially. When a stop codon is
encountered a termination factor (TF) binds to the mRNA and causes the
ribosome to dissociate, releasing the protein.
 A
Flash animation of translation in a eukaryote. A
Flash animation of translation in a eukaryote.
Practice Exercises (putting it all together)
- In this practice exercise you need to assemble the ribosome and
appropriate tRNA at the start codon for translation to begin. Review
the movie above if you need a refresher.
 Drag
the appropriate subunit of the ribosome and appropriate tRNA to the start
codon to begin translation. Drag
the appropriate subunit of the ribosome and appropriate tRNA to the start
codon to begin translation.
- In this practice exercise, the ribosome assembles at
the start codon, you need to choose the appropriate anticodon from a table
for translation to proceed. The anticodons are written 3' to 5', and
thus are antiparallel to the codons in the mRNA.
 Click
on the appropriate anticodon for translation to proceed. Click
on the appropriate anticodon for translation to proceed.
- In this final practice exercise you need to both
assemble the ribosome at the start codon, and then drag the appropriate tRNA
to match each codon for translation to occur.
 Drag
the appropriate subunit of the ribosome and appropriate tRNA to the start
codon to begin translation. Then drag each sequential tRNA to the
appropriate codon for translation to proceed. Drag
the appropriate subunit of the ribosome and appropriate tRNA to the start
codon to begin translation. Then drag each sequential tRNA to the
appropriate codon for translation to proceed.
- More interactive activities can be found at the following site on Translation.
|

