|
Current Level |
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
Previous Level |
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
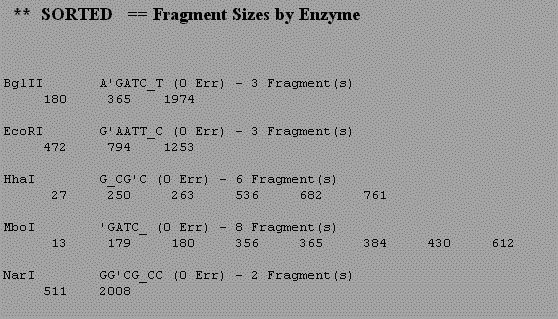
Log onto Biology Workbench and use NDJINN under Nucleic tools to obtain the human tPA cDNA sequence. Select the GenBank Primate database and search for the accession number 190031. Check the box next to the sequence and select import sequence. Now that you have a complete human tPA cDNA sequence stored in Biology Workbench we will translate the cDNA in all six reading frames. Import the longest open reading frame. Note that you are now in the Protein Tools section. To determine whether the protein has a signal peptide or other transmembrane domain, use the program GREASE. This performs a Kyte-Doolittle analysis of the protein and looks for 20 aa stretches of hydrophobic amino acids. Next look for motifs in the tPA amino acid sequence using the program PROSEARCH. This looks for things like glycosylation sites and active sites of enzymes. You can see a graphical analysis of the same data in ENTREZ. Go back to the window containing your DNA sequence in ENTREZ and in the upper right corner select links and then protein. This will give you the accession number for the protein sequence of tPA. Now go to the program CDART and enter this accession number. This will give a graphical display of the tPA protein with similar related proteins aligned below. Now go back to Biology Workbench and select Nucleic Tools and perform a restriction map on the sequence to determine where particular restriction enzymes will cut the cDNA. The authors used five different restriction enzymes in their cloning strategy. To understand this strategy we need to see where each of these enzymes cut the tPA cDNA. Follow the instructions in the restriction map site. Digest the tPA cDNA with the following enzymes. BglII, EcoRI, HhaI, NarI and MboI (the new name for Sau3A) Use the results you get to draw a map of tPA, indicating where each enzyme would cut. You should also get data indicating the sizes of fragments produced by each enzyme (an exampel is shown below). For each enzyme the restriction site is indicated as well. From the size of the restriction site, esitmate what the average size of a restriction fragment produced by this enzyme. Do your predictions match the results of the computer analysis?
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Practice Questions
|
|
|
|