|
Current Level |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Previous Level |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
BIOLOGY WORKBENCH contains a three programs for determining regions of hydrophobicity in a protein and potential membrane spanning domains. Enter the Biology Workbench and select your sequence under Protein Tools. Next select one of the programs listed below.
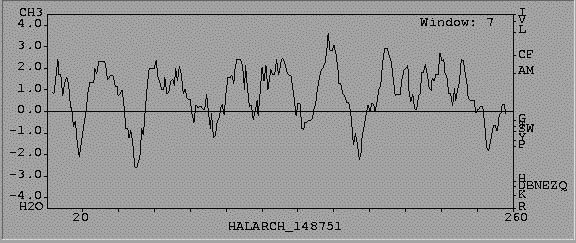
GREASE allows you to generate Kyte-Doolittle Hydropathy Profile. This does not predict secondary structure, so it will detect both alpha helix and beta sheet transmembrane domains. Numbers grater than 0 indicate increased hydrophobicity, numbers less than 0 indicate an increase in hydrophilic amino acids. Kyte Doolitle Hydropahty Profile.
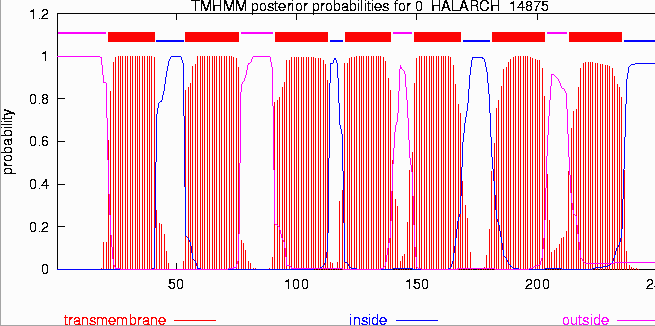
TMHMM allows you to predict the location of transmembrane alpha helices and the location of intervening loop regions. This program will also predict which loops between the helicies will be on the inside or outside of the cell or organelle. This program will not detect beta sheet transmembrane domains. It takes about 20 amino acids to span a lipid bilayer in an alpha helix. Programs can detect these transmembrane domains by looking for the presence of an alpha helix 20 amino acids long which contains hydrophobic amino acids. Transmembrane Helicies.
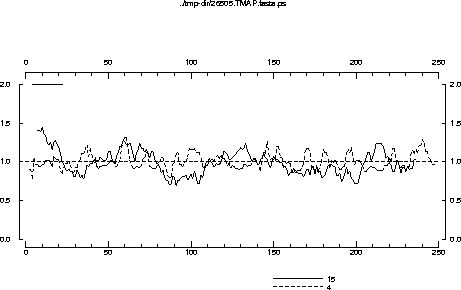
uses a Kyte-Doolittle Hydropathy Profile to detect transmembrane spanning domains. This does not require that the domain be an alpha helix, as in TMHMM. It also provides the amino acid numbers for the transmembrane domain. This is especially useful for detecting signal peptides. A signal peptide is a short hydrophobic sequence at the amino terminus of eukaryotic proteins targeted for the endoplasmic reticulum and often for secretion. TMAP output PREDICTED TRANSMEMBRANE SEGMENTS
|
|
|
|