|
Current Level |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Previous Level |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
The 1993 Nobel Prize in Medicine was awarded for the discovery of introns. When sequencing genomic DNA it is often difficult to identify a gene, or to determine which regions of a gene would encode for protein. With the many genome projects underway this is an important issue, and researchers use computer programs to look for several components of a gene. These can include long open reading frames, promoters, intron/exon splice sites, poly adenylation signals and CpG islands.
GENSCAN This program allows you to look for intron/exon splice sites, promoters and polyadenylation sequences. It will also link the various exons together to produce a long translated protein that you can use to search databases. Simply paste the genomic DNA sequence you wish to analyze into the box labeled DNA sequence and select Run GENSCAN.
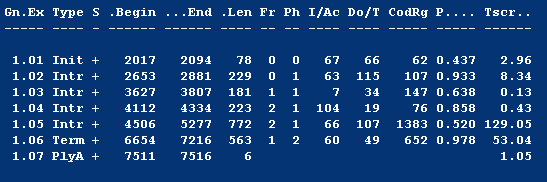
Analysis of Results A table of predicted exons and their translated amino acid sequence and coding DNA sequence (CDS) will be generated. The Table will indicate the beginning and end of each exon, an explanation of terms is provided below. |
 |
|||
 |
|||
|
The program will also link all of the exons together into a coding DNA sequence (like a cDNA) which will then be translated into protein. |
 |
|
If you select Predicted CDS and peptides under Print options, then the program will also display the coding sequence of DNA. |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
